🎉 JointJS has new documentation! 🥳
🎉 JointJS has new documentation! 🥳
This plugins imports a graph represented as an XML string in the GEXF format and makes it a JointJS graph.
The plugin contains only one function joint.format.gexf.toCellsArray(xmlString, makeElement, makeLink),
where xmlString is an XML string representing a graph in GEXF format, makeElement is a function that takes
an object with id, width, height and label properties and returns a JointJS shape for this node.
makeLink is a function that takes an object with source and target properties and returns
a JointJS link for that edge.
Include joint.format.gexf.js file into your HTML:
<script src="joint.format.gexf.js"></script>var cells = joint.format.gexf.toCellsArray(
someGEXF_XML_String,
function makeElement(attrs) {
return new joint.shapes.basic.Rect({
id: attrs.id,
size: { width: attrs.width, height: attrs.height },
attrs: { text: { text: attrs.label } }
});
},
function makeLink(attrs) {
return new joint.dia.Link({
source: { id: attrs.source },
target: { id: attrs.target }
});
}
);
graph.resetCells(cells);The Print plugin extends the joint.dia.Paper with the following method that, when called,
prepares the paper for printing and initiates printing using the browser print wizard:
print([options]) - prints the paper using the browser print dialog box.Where options is an object with the following possible values:
| sheet | object | Optional. Along with the sheetUnit, margin and marginUnit it defines the
output paper. sheet could be specified as an object: { width: [number], height: [number] }. It
defaults to size of the A4 - 210x297. This option
also sets the page orientation - landscape or portrait. For example A4 - landscape would be set as {
width: 297, height: 210 }
.
Example: 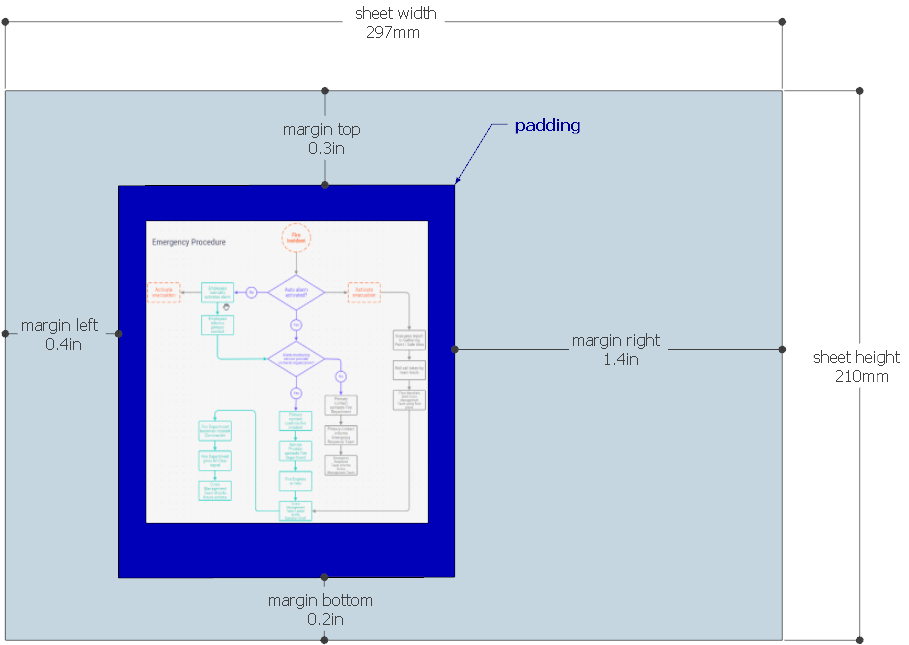
Please note, the |
|---|---|---|
| sheetUnit | string | Optional. Size unit for the sheet option. Supported units are mm, cm,
in, pt, pc. It defaults to mm
|
| area | object |
Optional. Custom area to be printed. Defined as {width: [number]: height: [number], x: [number], y:
[number] }. If the area is not defined, the whole graph is printed.
|
| ready | function | Optional. This callback function is triggered when the print content is ready for the actual print. At this moment it's possible to update the print content element (e.g. set some additional css styles) and pass this through. Or, it's also possible to cancel the print process. The prepared print content is a HTML element (multiple elements in case of the poster option). To cancel the print process pass falsy value into the readyToPrint callback (see the example below). This is useful if you need e.g. add a watermark or have a custom print preview UI widget.
|
| poster | boolean | object | Optional. Splits the area to be printed to pieces. Each piece will be printed on a separate page. poster can be defined either as { rows: [number], columns: [number] } or as { width: [number], height: [number] }. The first option (rows/columns) is a "table-style". It treats the print area to be a table and it divides it to defined amount of rows and columns. The width/height variant allows you to define the width and height of the piece. It defaults to false. |
| margin | number | object | Optional. The space on all sides of the paper area to be printed. The margin could
be also an object with the following properties for finer grained control of the margin on each side:
{ left: [number], top: [number], right: [number], bottom: [number] } |
| marginUnit | string | Optional. Size unit for the margin option. Supported units are mm, cm,
in, pt, pc. It defaults to in
|
| padding | number | object | Optional. This is applicable only if the option area is not set - when the whole graph is
printed. It's an extra space added to each side of the graph. The padding could
be also an object with the following properties for finer grained control of the padding on each side:
{ left: [number], top: [number], right: [number], bottom: [number] } |
Include print.css and joint.format.print.js files into your HTML:
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="print.css">
<script src="joint.format.print.js"></script>$('#print-btn').click(function() {
paper.print({
padding: 10,
sheet: { width: 297, height: 210 },
poster: false,
margin: 1,
marginUnit: 'in',
ready: function(printAreaElements, readyToPrint) {
printAreaElements.forEach(function($el) {
$el.find('#paper').css('border', 'none');
});
readyToPrint(printAreaElements)
}
});
});
If you'd like to add your custom text or logo to all the printed papers, you can use the following method in your CSS:
@media print {
body:before {
content: 'My Cool Company';
top: -5mm;
}
}This adds the text My Cool Company to the top of the printed document. For adding a logo image, just set
width, height and background-image properties on the :before
pseudo-element.
This plugin adds new methods to the joint.dia.Paper object for exporting paper to PNG and JPEG raster formats on
the client side:
| toPNG(callback [, options]) | Executes the callback function with a PNG data URI representing the content of the paper as the first parameter. |
| toJPEG(callback [, options]) | Executes the callback function with a JPEG data URI string representing the content of the paper as the first parameter. |
| toDataURL(callback [, options]) | The general version of two previous methods. Executes the callback function with a data URI string representing the content of the paper in specified MIME type as the first parameter. |
The available options are:
| width | number | Set the width of the image in pixels. |
| height | number | Set the height of the image in pixels. |
| size | number | Size multiplicator for generating raster images in a higher resolution. It expects a string in the form of [Number] + 'x' describing how many times the image width and height should be multipicated.
It defaults to '1x'.
|
| backgroundColor | string | The image background color. |
| padding | number | The space between the image border and the image content. It can also be an object with left, top, right and bottom properties
|
| type | string | The standard MIME type for the image format to return (only applies to toDataURL()).
|
| quality | number | The quality level of a JPEG image compression in the range of 0.0 to 1.0 (only applies to
toJPEG()).
|
| area | g.Rect | An area, that the resulting raster image should display. The value is an object, which contains x,y,width and height, describing the origin and the size of a rectangular area on the paper in the local coordinates. It defaults to the paper content bounding box - paper.getContentBBox() transformed into the local coordinates.
|
| useComputedStyles | boolean | The same behaviour as useComputedStyles in paper.prototype.toSVG(). |
| stylesheet | boolean | The same behaviour as stylesheet in paper.prototype.toSVG(). |
| beforeSerialize(SVGDocument, paper) | function | The same behaviour as beforeSerialize in paper.prototype.toSVG(). |
Note an exception 'dia.Paper: raster size exceeded' can be thrown if the raster size reaches the browser limits. In that case the raster size / resolution can be lowered through the size option e.g { size: '.5x' }.
Include joint.format.svg.js and joint.format.raster.js file into your HTML:
<script src="joint.format.raster.js"></script>(Note that this plugin requires the SVG Export.)
To get the plugin to work across all modern browsers include also canvg library and its dependencies. All these files are part of the Rappid toolkit, in the Raster/lib directory:
<script src="format/Raster/lib/rgbcolor.js"></script>
<script src="format/Raster/lib/StackBlur.js"></script>
<script src="format/Raster/lib/canvg.js"></script>paper.toPNG(function(imageData) { sendToServer(imageData); });
paper.toJPEG(function(imageData) { offerForDownload(imageData); }, {
width: 640,
height: 320,
quality: 0.7
});This plugins adds two new methods to the joint.dia.Paper object:
toSVG(callback[, opt]) - Converts the content of the paper to an SVG string and calls the callback with the SVG string as the first parameter.openAsSVG() - Opens a new window with SVG representing the content of the paper.Include joint.format.svg.js file into your HTML:
<script src="joint.format.svg.js"></script>paper.toSVG(function(svgString) {
sendToServer(svgString);
offerForDownload(svgString);
});The toSVG(callback[, opt]) method takes an option object opt with the following parameters:
| preserveDimensions | boolean | object | By default, the resulting SVG document has set width and height to 100%. If you'd like to have the dimensions to
be set to the actual content width and height, set preserveDimensions to true.
An object with width and height properties can be also used here if you need to define the export size explicitely.
|
| area | g.Rect | An area, that the resulting SVG should display. The value is an object, which contains x,y,width and height, describing the origin and the size of a rectangular area on the paper in the local coordinates. It defaults to the paper content bounding box - paper.getContentBBox() transformed into the local coordinates.
|
| convertImagesToDataUris | boolean | Converts all contained images into Data URI format. It defaults to false. |
| useComputedStyles | boolean |
When set to When set to |
| stylesheet | string |
A stylesheet (as string) can be provided and appended to the resulting SVG export. It defaults to |
| beforeSerialize(SVGDocument, paper) | function | A function called before the XML serialization. It may be used to modify the exported SVG before it is converted to a string. The function can also return a new SVGDocument. |
This plugins allows for import of a Microsoft Visio 2013 VSDX file and converting Visio Shapes to JointJS Cells, as well as exporting a JointJS Paper as a VSDX archive. Visio plugin is an independent module, and it supports both ES5 as well as newer, non-ES5 project environments.
Include all required dependencies into your HTML:
<!-- Rappid/JointJS dependencies: -->
<script src="lodash.js"></script>
<script src="jquery.js"></script>
<script src="backbone.js"></script>
<script src="rappid.js"></script>
<!-- plugin dependencies: -->
<script src="jszip.js"></script>
<script src="formula-parser.js"></script>
<script src="joint.format.visio.js"></script>At this point plugin is ready to use. Following example imports a vsdx project using default converter:
joint.format.Visio.VisioArchive.fromURL('network.vsdx').then(function(archive) {
var page = archive.document.getPages()[0];
var graph = new joint.dia.Graph();
var paper = new joint.dia.Paper({
el: document.getElementById('paper'),
model: graph,
interactive: false,
width: page.width,
height: page.height,
sorting: joint.dia.Paper.sorting.APPROX,
async: true,
frozen: true
});
page.getContent().then(function(content) {
var cells = content.toGraphCells();
graph.resetCells(cells);
paper.unfreeze();
});
});For non ES5 projects there's no additional installation required, simply import from @clientio/rappid-visio plugin module.
import { VisioArchive, types, VisioPageContent } from '@clientio/rappid-visio';Following documentation examples use a non-ES5 code.
VisioArchive and a chosen method, suited for the source type:
This basic example of how to import a Visio project and use it in JointJS application uses default import process.
As the default converter translates Visio Shapes as-is, the result might differ in JointJS in comparison to Visio.
// load a vsdx file and pick a page to work with
const { document: vsdDocument } = await VisioArchive.fromURL('./project.vsdx');
const [page0] = vsdDocument.getPages();
// load objects present on the VisioPage
const pageContent = await page0.getContent();
// use default converter to create JointJS Cells from Visio Shapes
const cells = pageContent.toGraphCells();
graph.resetCells(cells);
paper.setDimensions(page0.width, page0.height);For an example with mapping, which gives more control over how Visio Shapes are imported, see the Visio/demo/bpmn-import.
A basic export example, which uses default converter to translate JointJS Paper as-is.
Do mind, that results might differ between JointJS application and Visio (i.e. unmapped icons might not display properly).
// load Visio archive that will be used for export
const archive = await VisioArchive.fromURL('./project.vsdx');
const { document: vsdDocument } = archive;
// pick a page that will be the target for the export
const [page0] = vsdDocument.getPages();
// update page in the archive with JointJS Paper data using the default converter
await page0.fromPaper(paper);
// download archive using chosen method
const blob = await archive.toVSDX({ type: 'blob' });
util.downloadBlob(blob, 'project.vsdx');Config contains globally used flags controlling certain functionalities of the plugin.
To modify the plugin behavior, import config and toggle contained flags.
| evaluateFormulas | boolean |
Boolean controlling if formulas are evaluated when looking up a VisioCell value. Defaults to Formula parser is currently in early beta. Some parsed values might be different in comparison to value calculated by Visio. |
|---|
An enum containing all cell names supported by Visio 2013. This is useful i.e. when adding new cells to VisioShape.
An enum containing row types supported by Visio 2013. This is useful i.e. when creating own Geometry type section.
An enum containing section types supported by Visio 2013. This is useful when adding, modifying or removing a section.
An enum containing cell unit types supported by Visio 2013. When modifying or adding a cell, remember to set units
for the value, otherwise a project exported and opened in Visio might not work properly. Visio uses units
to properly evaluate the cell value.
util.fromPixels(value, units)
Convert a given value from pixels to the provided units.
units should be a valid numeric type supported by Visio (types.VisioUnitType).
| value | number | Numeric value that will be converted. |
|---|---|---|
| units | VisioUnitType |
Unit type of the target value.
Supported numeric unit types:
|
const inches = vsdUtil.fromPixels(96, VisioUnitType.IN); // 1util.isFontAvailable(font)
Return true if provided font is available for the application.
| font | string | array |
Function accepts either a string name of a single font or an array
of font names. If a string was provided, function will return true if the font is available in the
browser. Otherwise it will return false. If an array of font names was provided, an array
of true/false results will be returned in order of the provided collection of font names.
|
|---|
util.toPixels(value, units)
Convert the given numeric value to pixels. Function takes opt object in which a units
property can be defined. If no units is provided, types.VisioUnitType.IN is used by default.
| value | number | Numeric value that will be converted. |
|---|---|---|
| units | VisioUnitType |
Unit type of the source value. Defaults to VisioUnitType.IN.
Supported numeric unit types:
|
const px = vsdUtil.toPixels(1, VisioUnitType.IN); // 96
At the core of the plugin lies VisioArchive class, which is a bridge between Microsoft Visio and JointJS.
It's main purpose is to translate Visio vsdx archive into a VisioDocument instance.
A more complex example showcasing mapping to/from Visio Shapes can be found in the plugins demo directory.
async fromArrayBuffer(buffer)Load a Visio vsdx archive from an ArrayBuffer. This method returns a Promise.
const url = './project.vsdx';
const contentType = 'application/vnd-ms-visio.drawing;charset=utf-8';
const file = await fetch(url, { headers: { 'Content-Type': contentType }});
const arrayBuffer = await file.arrayBuffer();
const archive = await VisioArchive.fromArrayBuffer(arrayBuffer);async fromBase64(base64)Load a Visio vsdx archive from a base64 string. This method returns a Promise.
async fromURL(url)Load a Visio vsdx archive fetching it from a provided URL. This method returns a Promise.
const url = './project.vsdx';
const archive = await VisioArchive.fromURL(url);A blank project that can be used to test export process can be fetched from JointJS resources page.
The document property holds an instance of VisioDocument of an imported vsdx archive.
The source property holds the original archive used to create the VisioArchive instance. It's being stored as an ArrayBuffer.
async visioArchive.toVSDX([opt]])Use data stored in the VisioArchive instance to generate a vsdx file. This method will return a promise resulting in a vsdx file in a chosen format.
The toVSDX([opt]) method takes an object opt with the following parameters:
| type | string |
Format type in which the vsdx will be returned. By default 'blob' type is used. Other
accepted types are: 'base64', 'binarystring', 'array', 'uint8array', 'arraybuffer'
|
const blob = await visioArchive.toVSDX({ type: 'blob' });
joint.util.downloadBlob(blob, 'project.vsdx');A basic example of export process using default converter can be found in the plugin usage section.
VisioCell describes attributes of a single cell, and its API allows only for the lookup actions.
setCell method should be used to perform an update.
visioCell.eval()Return a calculated result based on cell value, units and formula.
Return a formula that the cell uses to calculate the value.
Return a cell name (one of VisioCellName enum values).
Return a unit type of the cell. Used by Visio and visioCell.eval() to properly evaluate the value.
Return a raw cell value. Raw cell value is given in the cell.units and returned as a string.
VisioConnect represents a connection between two Visio Shapes. It contains metadata describing source and target including which part of the Shape is used as an anchor.
An important concept to understand is that in Visio projects, a connection between two shapes consists of two entities: Connect and a Shape, represented by VisioConnect and VisioShape within the plugin. VisioConnect contains metadata about the connection. It also points to the shape that visually represents the connection, as well as source and target shapes.
String name of the VisioCell from which the connection originates.
Identifies the part of the Visio Shape from which a connection is made.
INT id of the source VisioShape.
visioConnect.getShape()Return a VisioShape representing the connection itself.
visioConnect.getSource()Return a VisioShape representing the connection source shape. In case there is no source shape, method will return null.
visioConnect.getTarget()Return a VisioShape representing the connection target shape. In case there is no source shape, method will return null.
String name of the VisioCell to which the connection is made.
visioConnect.toLinkAttributes(sourceElement, targetElement)Return JointJS Link attributes, based on the VisioConnect properties and a provided sourceElement and targetElement.
Identifies the part of the VisioShape to which a connection is made.
INT id of the target VisioShape.
The top-level model in the Visio archive structure, containing all the project file data.
VisioDocument is a starting point for both importing a Visio vsdx project, as well as exporting a JointJS project to a vsdx file. When importing a vsdx project, VisioDocument is used to navigate pages, page contents, master shapes etc. In export process, VisioDocument is helpful in instantiating VisioShapes based on VisioMaster shapes and finally building a vsdx file from the document contents.
visioDocument.getMasters()Return an array of VisioMaster instances present in the document.
visioDocument.getMastersIdMap()Return a Map of VisioMaster instances present in the document, using master id as the key.
visioDocument.getMastersMameMap()Return a Map of VisioMaster instances present in the document, using master name as the key.
visioDocument.getPage(pageId)
Return a VisioPage metadata object describing a single page with the given pageId. If page with given id doesn't exist, method will return undefined.
Metadata does not contain page contents. To load contents, use page.getContents() method.
| pageId | int | A unique integer page id number. |
To fetch metadata of a particular page do:
const archive = await VisioArchive.fromURL('./assets/vsdx/archive.vsdx');
const { document: vsdDocument } = archive;
const page1 = vsdDocument.getPage(0);To fetch a page that's used as a background for a particular page, simply do:
const archive = await VisioArchive.fromURL('./assets/vsdx/archive.vsdx');
const { document: vsdDocument } = archive;
const page1 = vsdDocument.getPage(0);
const bgPage = vsdDocument.getPage(page1.backPage);visioDocument.getPages()
Return an array of VisioPage metadata objects present in the loaded vsdx document. Metadata does not contain page contents.
To load contents of a particular page, use page.getContents() method.
getPages() can be useful i.e. for building project page listing.
VisioGeometrySection inherits from VisioIndexedSection.
Indexed section structures hold ordered rows collection.
visioGeometrySection.addRow(geometryRowType)
Add a named VisioRow to a geometry section rows collection. Provided geometryRowType must be
one of VisioRowType enum values. If no geometryRowType is provided, a row of type VisioRowTyp.RelMoveTo
will be added in case it's the first row, or VisioRowType.RelLineTo for any consecutive rows.
const [geometry0] = vsdShape.getGeometry();
geometry0.addRow(VisioRowType.MoveTo);
VisioIndexedSection inherits from VisioSection.
Indexed section structures order rows using an integer index. Order of rows is important.
Following sections use indexed row structure:
Character
Connection
Field
FillGradient
Geometry
Layer
LineGradient
Paragraph
Reviewer
Scratch
Tabs
visioIndexedSection.addRow()
Appends a VisioRow to an indexed section rows collection.
const scratch = vsdShape.getSection(VisioSectionType.Scratch);
scratch.addRow(); // add a row with next available indexvisioIndexedSection.getRow(index)
Return a VisioRow with a given index in a section with indexed structure.
If row doesn't exist, return null.
visioIndexedSection.removeRow(index)
Remove a row with the given index from an indexed section.
VisioMaster contains metadata of a Visio stencil item.
visioMaster.getIconBase64()Return a base64 data string containing a stencil item icon.
Return a unique, integer master id.
Return a name that by design in Visio is unique. Multiple instances of a same name in a stencil receive an additional ID appended to the name (i.e. "Master.12").
VisioIndexedSection inherits from VisioSection.
Named section structures hold unordered rows collection. Row names have to be unique.
Following sections use named row structure:
Actions
Control
Hyperlink
Property
ActionTag
User
visioNamedSection.addRow(rowName)
Add a VisioRow to a named section rows collection. Can not add a row with a given rowName
if a row with such name already exists.
const properties = vsdShape.getSection(VisioSectionType.Property);
properties.addRow('NewPropertyRow');visioNamedSection.getRow(rowName)
Return a VisioRow in a named section with a given rowName.
If row doesn't exist, return null.
visioNamedSection.removeRow(rowName)
Remove a row with the given rowName from a named section.
VisioPage contains metadata describing a page in a document. Its API allows to load contents of the page, as well as update the page data with JointJS Paper when exporting a project to vsdx format.
Return true if the page is marked as a background page. Background pages are oftentimes used to
show repetitive content on many foreground pages.
If the page uses a background page, return its id
async visioPage.fromPaper(paper [,opt])
page.fromPaper() method is used when exporting a JointJS project to a vsdx file format.
Before the vsdx archive is built, its pages should be updated with new content. This new content is built
using JointJS paper.
The below example updates visio archive with the contents of JointJS paper and uses default converter to
create a VisioShape for each JointJS Cell, as well as update project configuration.
Lastly, the updated archive is exported as a vsdx file.
const archive = await VisioArchive.fromURL('./project.vsdx');
const { document: vsdDocument } = archive;
const [page1] = vsdDocument.getPages();
await page1.fromPaper(paper);
const blob = await archive.toVSDX({ type: 'blob' });
util.downloadBlob(blob, 'project.vsdx');For a more robust example on the export flow with mapping, view demos/bpmn-export demo files.
The fromPaper(paper, [opt]) method takes JointJS paper, and an object opt with the following parameters:
| exportElement | function |
An |
| exportLink | function |
An |
async visioPage.getContent()Return a VisioPageContent instance containing page shapes.
Return page height in pixels.
Return a unique, integer page id.
Return page name as configured in Visio project.
Return page universal name as configured in Visio project.
Return page height in pixels.
VisioPageContent gives access to all instances of VisioShapes and VisioConnects present on the given page,
as well exposes an API useful in converting page contents to JointJS Cells using pageContent.toGraphCells([,opt]) method.
To work with page content, modifying shapes etc., loading VisioPageContent is always the first step. Provided API allows fetching any kind of entity that is part of the page content.
visioPageContent.getConnect(shapeId)Return a VisioConnect associated with the provided shapeId. If no such shape exists,
return undefined.
As VisioConnect contains connection metadata, it always points to the actual VisioShape that is a visual representation of the connection.
visioPageContent.getConnects()Return all VisioConnects present in the page content.
visioPageContent.getElementShapes()Return all VisioShape's that would be identified as Element in JointJS.
visioPageContent.getFonts()Return an array of fonts used by shapes on the page. If no fonts are defined, return an empty array.
visioPageContent.getForeignShape(path)Return VisioShape considered foreign (i.e. image), with the given path within the VisioArchive document.
If there is no shape for the given path, method will return undefined
visioPageContent.getForeignShapes()Return all VisioShapes considered foreign (i.e. images) from the page content.
visioPageContent.getLinkShapes()Return all VisioShape's that would be identified as Link in JointJS.
visioPageContent.getRootShape(id)Return a top-level VisioShape with the given id from the page content.
Return undefined if shape does not exist or is not a root shape.
visioPageContent.getRootShapes()Return all top-level VisioShape instances from the page content. Omit all the sub-shapes.
visioPageContent.getShape(id)Return a VisioShape with the given id.
visioPageContent.getShapes()Return all VisioShape instances from the page content.
visioPageContent.getUnsupportedFonts()
Return an array of fonts that are used by shapes on the page, however are not supported by the application.
If all fonts are supported, return an empty array.
visioPageContent.toGraphCells([,opt])Method used to convert contents of a Visio project page to JointJS Graph Cells. Its main usage is in the
import process of a vsdx file into a JointJS application.
The toGraphCells([,opt]) method takes an object opt with the following parameters:
| ignoreNonPrinting | boolean |
Control if shapes marked in Visio project as |
| ignoreSubShapeConnects | boolean |
Control if connections originating from or targeting nested shapes should
be imported or not. Defaults to |
| importShape | function |
For each |
| importConnect | function |
|
| importLabels | function |
If VisioShape identified as a connection contains a text, it is considered a label for that connection. If this function is not used, the default converter will be used to create link labels.
Labels can be handled using |
| importImage | function |
Foreign shapes, i.e. images, can be handled separately with |
| onImagesLoad | callback |
Although |
A full example of usage can be found in demo/bpmn-import directory.
VisioRow inherits from VisioSheetObject abstract class,
exposing an API used in cells manipulation: getOwnCellNames, getCell, setCell and removeCell.
VisioRow is contained within a VisioSection. Each row contains
cells describing a VisioSection that the row is contained in.
Available cells are defined by a section type row. More information can be found in the Visio documentation.
If the row is part of a indexed VisioSection, returns an integer index of the row.
If the row is part of a named VisioSection, returns a name of the row.
Return type of the row or undefined if there is no type set.
As an example, type is used by Geometry section rows to indicate what kind if drawing action it describes, i.e. 'LineTo'.
VisioShapes and VisioRows contains VisioSections that describe them using cells.
VisioSection is an abstract class that VisioNamedSection and
VisioIndexedSection inherit from. It provides an API to look-up VisioRows.
Classes that inherit from it expose API to fetch and modify rows.
| Named |
Named structures identify rows by a Actions
Control
Hyperlink
Property
ActionTag
User
|
|---|---|
| Indexed |
Indexed structures order rows using an integer index. Order of indexed rows is important. Character
Connection
Field
FillGradient
Geometry
Layer
LineGradient
Paragraph
Reviewer
Scratch
Tabs
|
visioSection.getRows()
Return an array of VisioRows the section contains. If none exist, return an empty array.
Return type of the section. Each section type has one of the two row structures, either 'Indexed' or 'Named'.
VisioShape inherits from VisioSheetObject abstract class,
exposing an API used in cells manipulation: getOwnCellNames, getCell, setCell and removeCell.
visioShape.fromMaster(master, page)
Return a new VisioShape created from a provided master and on a provided page.
Example below shows typical case when loaded archive is used as an export target, so it's used both as a source of
masters and the target for the created VisioShapes.
const archive = await VisioArchive.fromURL('./project.vsdx');
const { document: vsdDocument } = archive;
const [page0] = vsdDocument.getPages();
// pick a stencil master
const masters = vsdDocument.getMastersNameMap();
const [master0] = masters['Master Name'];
// create a raw shape based on a stencil Master
const vsdShape = await VisioShape.fromMaster(master, page0);visioShape.addSection(sectionType)
Add a new VisioSection (either VisioIndexedSection or VisioNamedSection) based on the given sectionType.
In case it is a named section that already exists, new one will not be added. New indexed section will be appended at the end of the given collection
with an index incremented from the previously highest index.
// add a custom properties section
vsdShape.addSection(types.VisioSectionType.Property);visioShape.getAncestorShapes()
Return an array of ancestor VisioShapes of the shape, ordered starting with highest level.
visioShape.getComputedGeometry()
Return an array of sections merged from own and inherited geometries. If there is no geometry sections defined
on either shape or the master, return an empty array.
visioShape.getComputedSection(type)
Return a section merged from own and inherited from master section data. If section of the type
does not exist on either, return null.
If the given type is VisioSectionType.Geometry, return results of visioShape.getComputedGeometry().
visioShape.getConnect()
Return a VisioConnect of the shape. If shape does not have a connect pointing to it, return null.
visioShape.getGeometry()
Return an array shapes own geometry sections. If none is defined, return an empty array.
async visioShape.getImage()
Return an image object containing following properties:
| absolutePath | string | File path within the visio archive. |
|---|---|---|
| file | string | File name of the image. |
| extension | string | File extension of the image. |
| base64 | string | A base64 representation of the image. |
| selector | string | Image element selector. |
visioShape.getMaster()
Return a VisioMaster for a shape. Return null if the shape was not created from a stencil master.
visioShape.getOwnSectionNames()
Return an array of section names defined for the shape.
visioShape.getPageAngle()
Return a number describing shape angle to the page.
visioShape.getPageBBox()
Return a g.Rect describing the shape bbox on the page.
visioShape.getPagePosition()
Return a g.Point describing position of the shape on the page.
visioShape.getPageZIndex()
Return an int describing the shape z-index on the page.
visioShape.getRootShape()
Return the VisioShape that is a root shape for the given shape, or the visioShape itself if it is a root shape.
visioShape.getSection(type)
If an own section of type exists on the shape, return it. If a section does not exist on the shape, return null
Own sections are defined for the shape and set values override sections inherited from master shape.
If the given type is VisioSectionType.Geometry, return results of visioShape.getGeometry().
visioShape.getSectionNames()
Return an array of all section names available for the shape, including inherited ones.
visioShape.getSubShapes()
Return an array of all shapes nested within the given visioShape.
visioShape.getText()
Return a string representing shape text if one exists. If none is defined, return empty ''.
visioShape.hasImage()
Return true if the shape contains an image.
A unique, integer shape id.
visioShape.isOneDimensional()
Return true if the shape is considered 1-D (one-dimensional) in Visio. Such shapes contain beginX, beginY,
endX, endY cells. Return false if shape is considered 2-D.
masterId points to a master given shape was created from.
A string name of the shape.
visioShape.removeSection(sectionName, sectionIndex)
If a named section is being removed, only the sectionName parameter is required. For indexed section, a second
parameter, sectionIndex has to be provided. sectionIndex defaults to 0 if none is provided.
// remove property section
vsdShape.removeSection(types.VisioSectionType.Property);
// remove geometry section with index 2
vsdShape.removeSection(types.VisioSectionType.Geometry, 2);visioShape.setText(text)
Update shape text with given text. Do mind this will override the existing text.
visioShape.toElementAttributes()
Return JointJS dia.Element attributes created from the shape. It's particularly useful when using custom
Element instead of the one used by the default converter.
A string type of the shape, i.e. 'Shape' or 'Group'.
VisioSheetObject is an abstract class that allows for manipulation of cells within an object with sheet.
Classes inheriting from VisioSheetObject are VisioShape and VisioRow.
Any cells manipulation should be done only using the VisioSheetObject API.
Cell names are case-sensitive and should follow camel-case naming convention, while the name property in the
cell object uses pascal-case naming convention. Having that difference in mind, when using getCell method,
always use camel-case names, otherwise undefined will be returned.
Each cell is an object with name, value properties. Optionally formula and units can be defined.
sheetObject.getCell(cellName)Return a cell object with the given cellName. If cell with given name does not exist, return undefined.
cellName is case sensitive and should use camel-case naming convention.
console.log(vsdShape.getCell(VisioCellName.PinX));
// {value: "1", units: "IN", name: "PinX"}sheetObject.getOwnCellNames()Return an array of cell names defined as own for the sheet object. Does not include inherited cell names.
sheetObject.removeCell(cellName)Remove cell with the given cellName from the sheet object. cellName is case sensitive and should use camel-case naming convention.
vsdShape.removeCell(VisioCellName.PinX)sheetObject.setCell(cellName, cellAttributes)setCell allows for adding or updating a cell within the sheet object. Important thing to note is that
knowledge about Visio Cells is required to properly set cells in certain scenarios, i.e. units might be required
to properly evaluate the value in Visio.
Passing null as any of the cellAttributes will remove the attribute from the cell,
which will in return fallback to inherited value. If the intention is to override any attribute, set it to an empty string,
i.e. {formula:''}. Not passing any of the attributes will skip them, and existing ones
will be kept.
| cellName | string |
cellName should use camel-case naming of cells. Full list of accepted cell names
can be found in Visio documentation.
|
|||||||||
| cellAttributes | object |
|
Below code will update width cell (or create it if it doesn't exist), setting value to '1',
units to 'IN' and inheriting the formula.
// shape cell
vsdShape.setCell(VisioCellName.Width, { value: '1', units: VisioUnitType.IN });
// property section row cell
vsdRow.setCell(VisioCellName.Value, { value: '1', formula: null, units: VisioUnitType.BOOL });